** 공유가 아닌 개인 공부에 목적을 둔 글입니다
** 설명이 불충분할 수 있으며 잘 정리된 글이 아닐 수도 있습니다
Servlet 의 Lifecycle
package exam;
// import 생략
@WebServlet("/LifecycleServlet")
public class LifecycleServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public LifecycleServlet() {
System.out.println("LifecycleServlet 생성!!");
}
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("init 수정 호출!!");
}
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("destroy 호출!!");
}
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("service 호출!!");
}
}
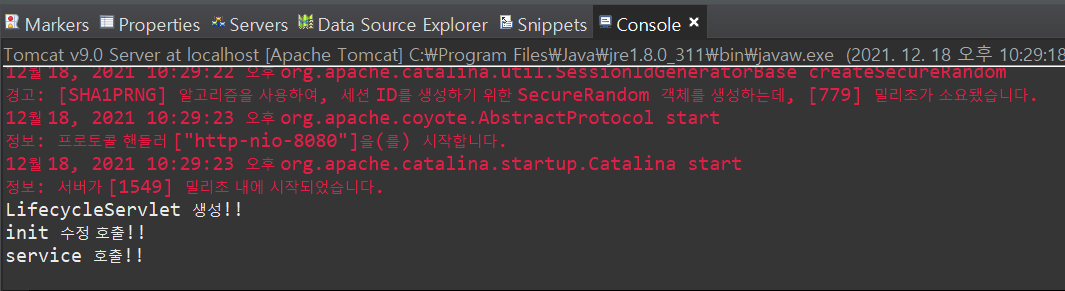
최초로 서버를 실행하면 서버는 해당 클래스가 메모리에 있는지 확인 후 없으면 생성자를 호출해 객체를 생성하고
메모리에 올린다 => LifecycleService 생성!!
그후 init() 메소드 호출 -> service() 메소드를 호출한 것을 볼 수 있다
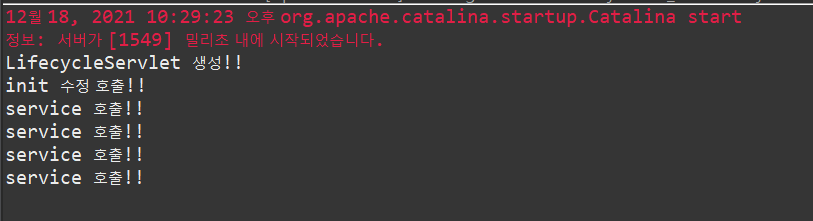
다시 브라우저를 새로고침해서 새로운 요청을 보내면 service() 메소드만 호출이 되는데
서버에 서블릿 객체는 하나만 존재하도록 되어있어서 이미 존재하면 새로 만들지 않고 service() 만 호출하게 된다
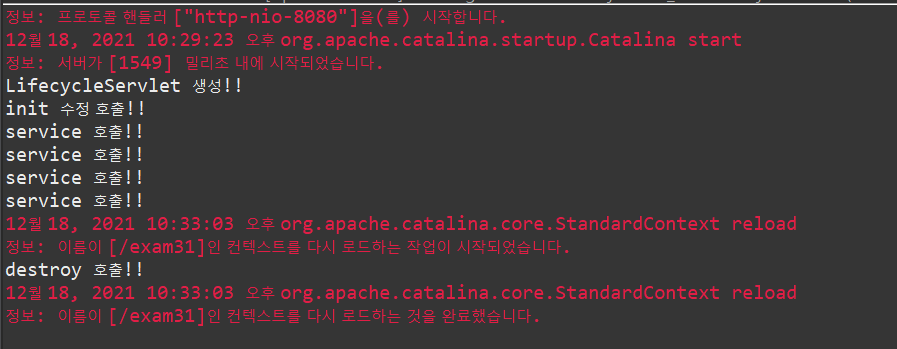
서블릿을 수정해서 웹 어플리케이션이 갱신되거나
혹은 브라우저를 멈추면 WAS가 종료되면서 destroy() 가 호출된다
service() 메소드의 오버라이드
그런데 service() 메소드와 doGet(), doPost() 등의 메소드들은 모두 HttpServlet 클래스를 상속받고 있다
즉 굳이 service() 를 직접 통하지 않아도 doGet() 등의 메소드들은 HttpServlet 클래스의 service 메소드를 실행할 수
있다는 것이다
WAS 는 꼭 service() 를 호출하고서 동작하는데, serice() 메소드가 없어서 service() 를 실행할 수 없는 것처럼 보여도
doGet() 같은 메소드들은 service() 메소드와 마찬가지로 HttpService 를 상속하고 있기 때문에
Servlet 의 부모클래스인 HttpServlet 의 service() 가 실행됨으로써 작동한다
package exam;
// import 생략
@WebServlet("/ten")
public class TenServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public TenServlet() {
super();
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.print("<h1>1-10까지 출력 </h1>");
for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) {
out.print(i+"<br>");
}
out.close();
}
}
바로 이전 글에서 사용했던 코드인데 가져왔다
위와 같은 코드에서 service() 가 없어도 정상적으로 작동되는 것을 확인할 수 있다

